The Birth of Bitcoin
Bitcoin was introduced in 2009 as a revolutionary creation by an individual (or group) operating under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Fundamentally, Bitcoin is a decentralized, digital currency designed to function independently of any central authority, whether governmental or financial.
Key Attributes of Bitcoin
Bitcoin boasts several distinctive features that distinguish it in the world of finance:
1. Decentralization: Bitcoin operates through a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries like traditional banks. Transactions transpire directly between users.
2. Blockchain Technology: All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on an open ledger known as the blockchain. This ledger is immutable and transparent, ensuring the integrity of transactions.
3. Limited Supply: Bitcoin adheres to a finite supply, capped at 21 million coins. This scarcity is hardcoded into its protocol, rendering it a digital equivalent of gold.
4. Security: Bitcoin transactions are safeguarded via intricate cryptographic techniques. Ownership of Bitcoin is established through private keys, delivering robust security against fraudulent activities.
5. Digital Gold: Frequently referred to as "digital gold," Bitcoin is often considered a store of value. Many view it as a hedge against inflation and economic turbulence.
1. Decentralization: Bitcoin operates through a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries like traditional banks. Transactions transpire directly between users.
2. Blockchain Technology: All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on an open ledger known as the blockchain. This ledger is immutable and transparent, ensuring the integrity of transactions.
3. Limited Supply: Bitcoin adheres to a finite supply, capped at 21 million coins. This scarcity is hardcoded into its protocol, rendering it a digital equivalent of gold.
4. Security: Bitcoin transactions are safeguarded via intricate cryptographic techniques. Ownership of Bitcoin is established through private keys, delivering robust security against fraudulent activities.
5. Digital Gold: Frequently referred to as "digital gold," Bitcoin is often considered a store of value. Many view it as a hedge against inflation and economic turbulence.
The Bitcoin Halving
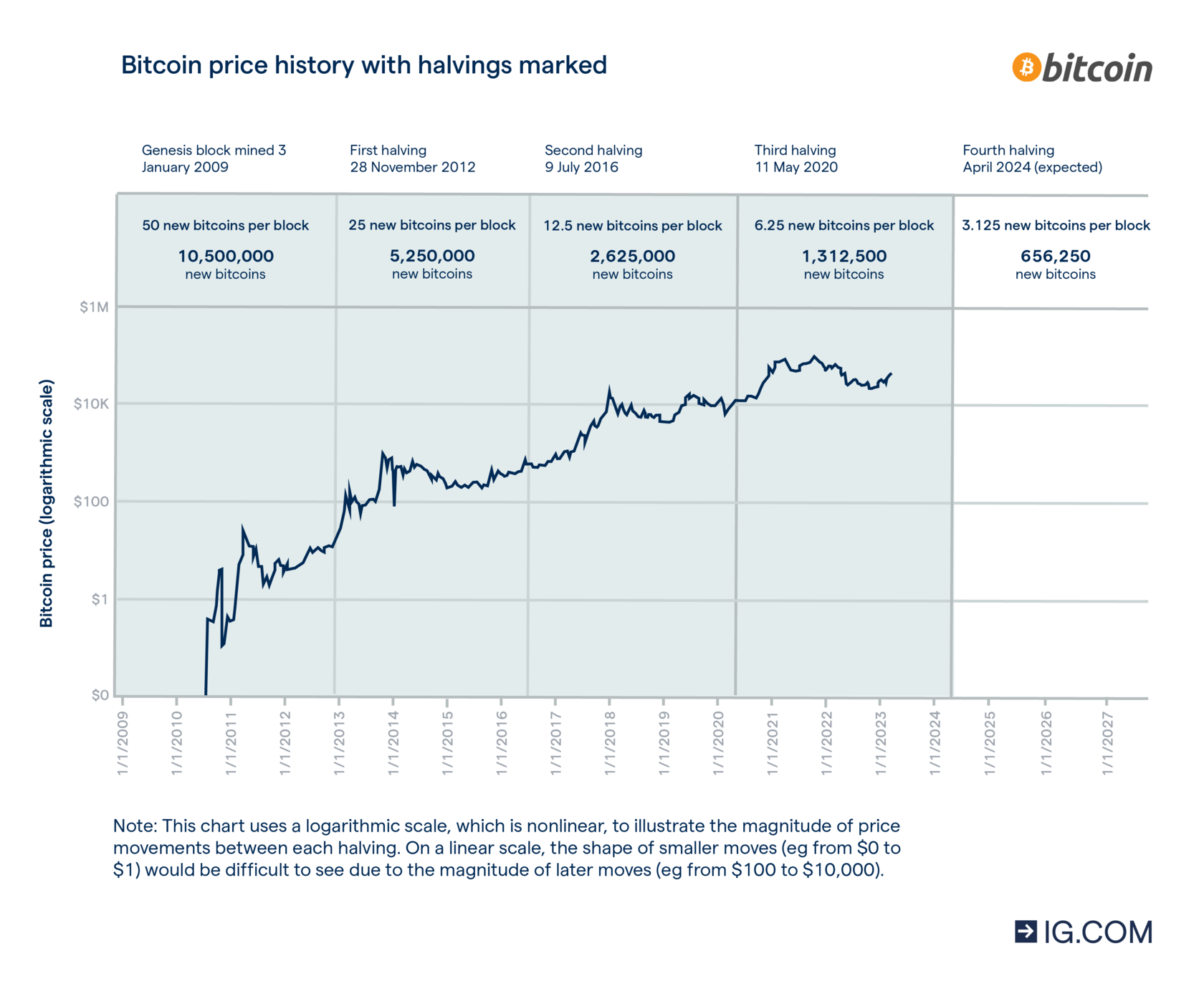
One of Bitcoin's distinctive features is the "Bitcoin halving," which occurs approximately every four years. During a Bitcoin halving, the number of new Bitcoins created and earned by miners for validating transactions is reduced by half. The most recent halving took place in May 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 Bitcoins to 6.25 Bitcoins.
Bitcoin Ecosystem
Bitcoin is not solely a digital currency; it signifies a comprehensive ecosystem. Here are some integral components:
1. Wallets: Bitcoin wallets are digital instruments for storing, sending, and receiving Bitcoin. They are available in a variety of formats, from online wallets to hardware devices.
2. Mining: Bitcoin mining encompasses the validation of transactions and their inclusion in the blockchain. Miners receive compensation through newly created Bitcoin and transaction fees.
3. Exchanges: Bitcoin can be bought, sold, and traded on cryptocurrency exchanges, where its value fluctuates in response to supply and demand.
4. Adoption: Bitcoin is increasingly recognized as a mode of payment by various businesses and even governments. Its mainstream acceptance continues to expand.
1. Wallets: Bitcoin wallets are digital instruments for storing, sending, and receiving Bitcoin. They are available in a variety of formats, from online wallets to hardware devices.
2. Mining: Bitcoin mining encompasses the validation of transactions and their inclusion in the blockchain. Miners receive compensation through newly created Bitcoin and transaction fees.
3. Exchanges: Bitcoin can be bought, sold, and traded on cryptocurrency exchanges, where its value fluctuates in response to supply and demand.
4. Adoption: Bitcoin is increasingly recognized as a mode of payment by various businesses and even governments. Its mainstream acceptance continues to expand.
Why Bitcoin Matters
Bitcoin's significance transcends its technical aspects. It represents a departure from traditional financial systems, extending financial inclusion to the unbanked and granting individuals control over their financial assets.
As the cryptocurrency landscape evolves, comprehending Bitcoin constitutes a fundamental first step. It embodies not merely a digital asset but also a paradigm shift in finance and economics. For further illuminating articles on cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, visit Coinbild.club.
As the cryptocurrency landscape evolves, comprehending Bitcoin constitutes a fundamental first step. It embodies not merely a digital asset but also a paradigm shift in finance and economics. For further illuminating articles on cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, visit Coinbild.club.
Disclaimer: This blog post serves informational purposes only and should not be regarded as financial advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry inherent risks, necessitating comprehensive research and consultation with professionals before investing.
